Healthcare data breaches keep climbing. In 2024 alone, attackers exposed 275 million patient records—82 percent of Americans—according to HHS breach-portal data summarized by HIPAA Journal.
Because every leaked record can trigger lawsuits and seven-figure fines, clients now screen you for HIPAA compliance before any code push or server hardening. This guide shows the promises, controls, and proof you’ll need so your invoice—and your reputation—survive an audit.
Handle PHI for a client, even once, and the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) classifies you as a business associate. That status gives OCR the same power to audit and fine you that it applies to hospitals.
Penalties add up fast. The penalties for HIPAA violations include civil monetary penalties ranging from $141 to $2,134,831 per violation, depending on the level of culpability. OCR has proved it will act: a cloud-services contractor paid $80,000 after ransomware exposed 31,000 patient records.
Clients share that liability, so they vet contractors as carefully as surgeons check sterile tools. Arrive with a signed Business Associate Agreement, proof of past HIPAA projects, and a crisp plan for encryption, least-privilege access, and 24-hour breach reporting. Position yourself as a partner in risk reduction, and you protect patient trust and your income.
A covered entity generally may not disclose PHI to a business associate without a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) in place (see 45 CFR §164.308(b), §164.502(e), and §164.504(e)).In February 2024, the OCR announced a $4.75 million settlement with Montefiore Medical Center. For audits, you can streamline evidence gathering with automated HIPAA evidence collection—for example, according to Vanta, their platform can automate up to 85% of required evidence. Note that the 60-day breach notification deadline comes from federal rules (45 CFR §164.404), not the BAA itself.
Most healthcare NDAs forbid naming the client. Honor that promise with disciplined habits. Use encrypted email, restricted Slack channels, and prohibit screenshots in slide decks.
Clients also look for cyber liability coverage. A 2024 survey of risk managers revealed that less than 20% are carrying cyber coverage, in contrast to 60% with property insurance. Small clinics pay a median $2,200 per year for $1 million in limits, a bargain compared with recent OCR fines. Health Fitness Corporation reached a settlement with the HHS Office for Civil Rights for failing to conduct a thorough risk analysis, related to a server misconfiguration. The settlement was announced in December 2025.
Expect an indemnification clause. If your code leaks records, you will share the cost. Keep scope tight, log every change, and align testing with the BAA. With solid documents and a disciplined process, the “vendor risk” headline loses power. According to the HHS OCR, in 2024, most protected health information (PHI) data breaches reported were the result of hacking incidents targeting non-hospital health care providers, including third-party service and software providers.
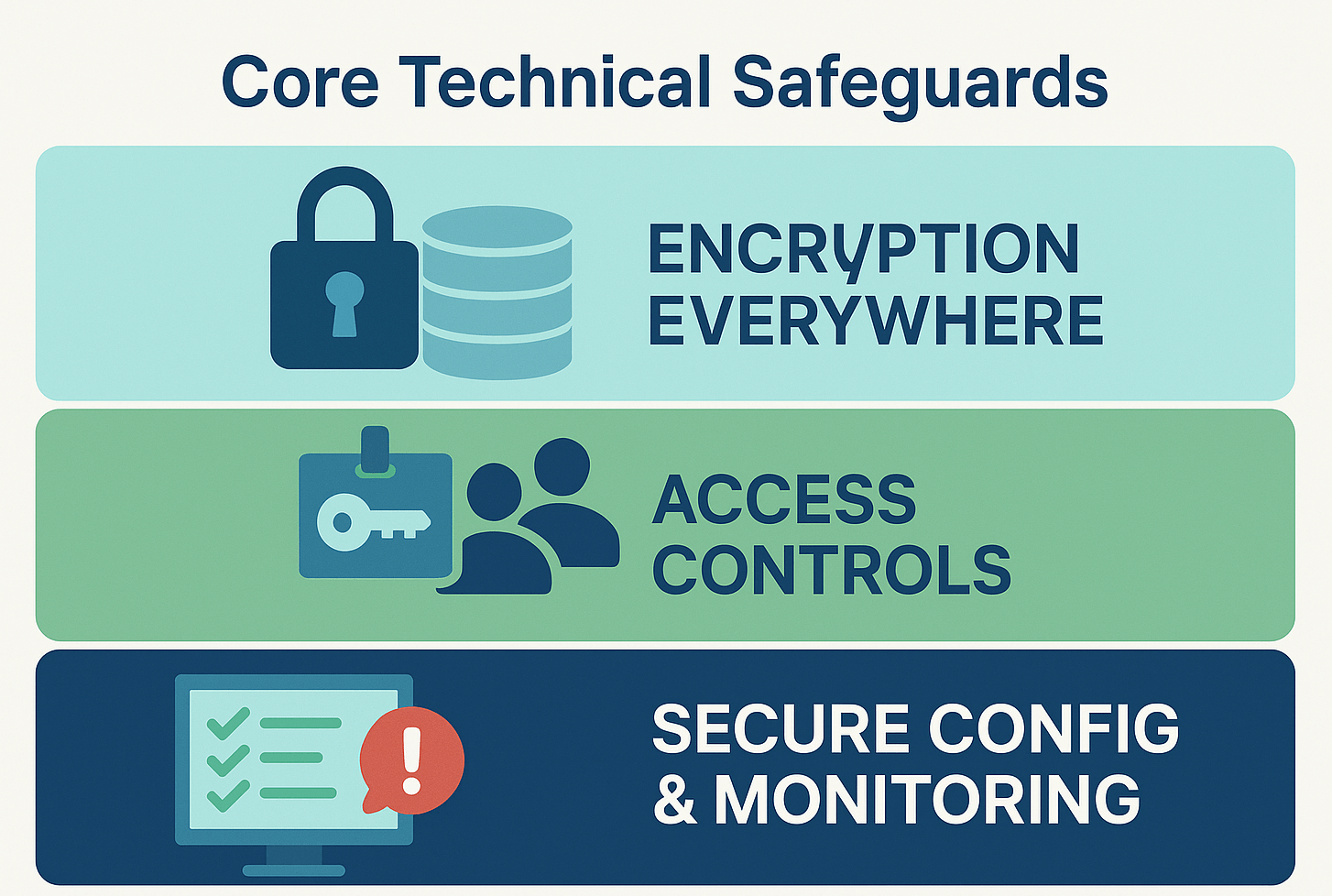
HIPAA’s Security Rule requires encryption of ePHI “at rest” (45 CFR §164.312(a)(2)(iv)) and “in transit” (§164.312(e)(2)(ii)) whenever it is reasonable and appropriate. A January 2025 proposal seeks to remove the “addressable” loophole and list encryption as a baseline control for every covered entity and business associate.
Data at rest. Enable AES-256 on every database, object store, and backup. Rotate primary keys every 12 months, as NIST SP 800-57 advises, and store them in an HSM isolated from production workloads. In 2020, Lifespan paid $1.04 million after a stolen, unencrypted laptop exposed 20,431 records, proving one device can cause seven-figure fines.
Data in transit. Require TLS 1.3 for all web and API traffic, and disable legacy ciphers such as 3DES and RC4. The White House's 2024 cybersecurity strategy emphasizes the importance of encryption, including for data in transit. The strategy was released in response to the growing threat of cyberattacks.
Continuous verification.Vanta; its GitHub and AWS connectors watch every commit and infrastructure change and fail the build whenever a resource tag reads encryption = false. Vanta also snapshots configuration drift each hour and stores evidence auditors can accept. Follow that with daily scans for public buckets or port 445 exposures and send a weekly diff to the client; evidence speaks louder than promises.
Lead with strong encryption, and every other safeguard falls into place. A lost drive stays unreadable, a packet sniffer grabs gibberish, and auditors review clear key-management logs, not excuses.
Encryption hides data, but access controls decide who can read it. HIPAA’s Technical Safeguards require a unique user ID (§164.312(a)(1)), automatic log-off (§164.312(a)(2)(iii)), and audit controls (§164.312(b)). Here is how that looks day to day.
Identify every human and service. Issue one credential per person or micro-service, then enforce multifactor authentication (MFA). The 2024 Change Healthcare ransomware attack exposed the data of approximately 190 million people. UnitedHealth Group, Change Healthcare's parent company, reported spending $3.1 billion in response to the attack in 2024.
Lock roles to need-to-know. Doctors see their patients, billing staff see payments, and no one else accesses either set. Map IAM roles to HL7 job codes or the client’s HR system, then auto-reconcile each week.
Time out idle sessions. NIST SP 800-53 caps inactivity at 30 minutes unless clinical workflow requires less. A laptop that self-locks turns a shoulder-surfing risk into a blank screen.
Make every click auditable. Centralize logs and alert on privilege escalation or exports larger than 1,000 rows. Investigators should be able to replay events frame by frame.
With these guardrails in place, a stolen password slows attackers instead of opening the door.
Default images launch fast but leak data just as quickly. Misconfigurations are a leading cause of breaches. In 2024, 60% of organizations experienced cloud-related security incidents, with 88% of data breaches caused by human error.
Harden first, store later. Close every unused port, delete demo accounts, and remove sample code before importing a single patient record. Map each server to the latest CIS Benchmarks and record the hash in version control.
Patch on a clock, not a whim. Follow CISA’s binding directive: 15 days for critical CVEs, 30 days for highs. Automate weekly reboots for low-risk packages and keep an emergency window for zero-days.
Detect drift. Feed configuration snapshots into a policy-as-code tool such as Open Policy Agent. Alert if an S3 bucket flips to public or an IAM role gains s3: wildcard rights.
With a secure-by-default, continuously monitored stance, misconfigurations remain dashboard blips, not headline events.
HIPAA’s audit-control rule (§164.312(b)) asks one question: Can you prove who touched which record and when?
Collect everything, centralize fast. Stream logs from cloud, on-prem, and mobile workloads into a single SIEM. Tag each event with user ID and PHI object so searches take seconds, not hours.
Alert on behavior, not just failures.
According to a 2024 Sophos report, ransomware attacks against healthcare organizations are at a four-year high, with 67% of surveyed organizations experiencing an attack in the past year. Cutting that dwell time to hours protects revenue and patient trust.
Make evidence immutable. Store logs in WORM or object-lock storage for at least 90 days hot / 7 years cold. Auditors now expect that pattern.
A clear dashboard then turns security into visible value: executives see blocked attacks, engineers spot drift, and you sleep through the night.
Lost or stolen devices still bring costly HIPAA penalties. Rhode Island’s Lifespan paid $1.04 million in 2020 after an unencrypted laptop with 20,431 records disappeared. HIPAA’s physical-safeguards standard (§164.310) applies to every contractor’s home office, so treat your hardware like a roaming data center.
Lock the box. Enable full-disk AES-256 encryption and biometric login, and set auto-lock to 15 minutes or less, per NIST SP 800-53 IA-11.
Travel like evidence matters. Carry laptops in tamper-evident sleeves and keep them out of checked luggage. Use data-only USB-C cables or a vetted dock because public chargers can deliver “juice-jacking” payloads.
Paper is still PHI. Print only when necessary, store documents in a locked drawer, and destroy them with a cross-cut shredder the same day.
A tight device routine removes the last physical gap attackers still exploit.
HIPAA does not stop at installing controls. §164.308(a)(8) requires a periodic technical evaluation to prove that safeguards still work. The numbers explain why:
Start with machines. Run automated scans on every commit, catch stale libraries, open ports, and weak ciphers. Fail the build whenever a CVSS score exceeds 7.0.
Bring in humans. Schedule a focused penetration test at least once a year or after any material change. Map test cases to HIPAA risks such as broken access control, SQL or NoSQL injection, and unencrypted backups.
Track and close. Log each finding in the risk register with severity, owner, and due date, and require proof of the fix before closure.
Retest and attest. Verify high-severity fixes within 15 days, then issue a short attestation memo the client can show auditors. This loop turns security from a quarterly scramble into a steady, provable heartbeat.
HIPAA makes a security risk analysis mandatory. §164.308(a)(1)(ii)(A) requires every covered entity and business associate to “conduct an accurate and thorough assessment” of risks to ePHI. By the end of 2024, OCR had collected over $9 million through fourteen resolved actions, which included settlements and final determinations.
Map the data flow end to end. Document where ePHI is created, stored, and transmitted. Tag each waypoint with likelihood and impact scores to surface high-risk intersections.
Prioritize fixes with the client. Encrypt the orphaned S3 bucket, close firewall ports, tighten IAM roles, and add off-site backups. Assign every control an owner and a due date so nothing lingers.
Translate findings into business language. Executives focus on downtime cost and penalty exposure, not CVE numbers. A concise, two-page brief answers three questions: What could go wrong? What would it cost? How do we reduce it?
Update the assessment at least once every 12 months, or after any major system change, and keep the paperwork ready for auditors who expect proof, not promises.
HIPAA’s administrative safeguards begin with written policies (§164.308(a)(1)(i)). A Proofpoint and Ponemon Institute survey found that 93% of surveyed healthcare organizations experienced at least one cyberattack in the past 12 months, and nearly three-quarters of respondents who experienced an attack reported disruptions to patient care. Documents alone will not protect records.
Keep them short and specific. Review existing binders; if they overlook remote work or mobile clinics, rewrite. When none exist, create lean playbooks that cover access control, incident response, and media disposal, and tag each one to its HIPAA citation.
Socialize in minutes, not manuals. A ten-minute Slack walkthrough, a one-page wiki quick-start, and an automatic prompt when someone requests PHI access deliver steady, bite-size reminders.
Let tooling police the edge cases. Continuous integration blocks merges that fail security scans. Mobile-device management refuses email on unencrypted laptops. Automation turns requests into required safeguards.
Revisit policies every twelve months, or after any major system change, and record executive sign-off for auditors. When rules match the workflow and software enforces them, compliance becomes habit and patients stay protected.
HIPAA’s Security Rule (§164.308(a)(5)) requires security-awareness training for every “workforce member,” contractors included. The need is clear: phishing caused sixteen percent of healthcare breaches in 2025 (HIPAA Journal roundup).
Kick-start, then drip. Deliver a twenty-minute onboarding that covers what counts as PHI, common breach paths, and the twenty-four-hour internal-report clock. After launch, post one micro-lesson each week, tied to real headlines or near-miss stories, to keep risk top of mind.
Measure and prove. Track attendance, collect e-signatures, and archive decks in the compliance folder. Run quarterly phishing simulations and aim to cut click-through rates below five percent, the benchmark KnowBe4 cites for mature programs.
Make culture the control. When a junior developer asks in Slack, “Is it safe to push this log file?” the program is working, and auditors can see the evidence. Ongoing awareness turns every team member into a human intrusion-detection sensor.
HIPAA codifies the paper trail. §164.316(b)(1) requires you to keep security-program records for at least six years. OCR's 2024 enforcement actions highlighted the importance of thorough documentation, with several settlements resulting from failures to maintain adequate records.
Log every change the moment it happens. Create one ticket ID, add a one-line summary, and link proof such as a screenshot, config diff, or e-signature. Simple beats are verbose.
Report weekly. Send an executive snapshot of open risks, resolved items, and deadlines. When leadership shares it, compliance looks like progress instead of paranoia.
Package the evidence. At project close, compress risk assessments, BAAs, scan reports, training logs, and a signed attestation. Store the bundle in WORM or object-lock storage for six years hot and then archive cold.
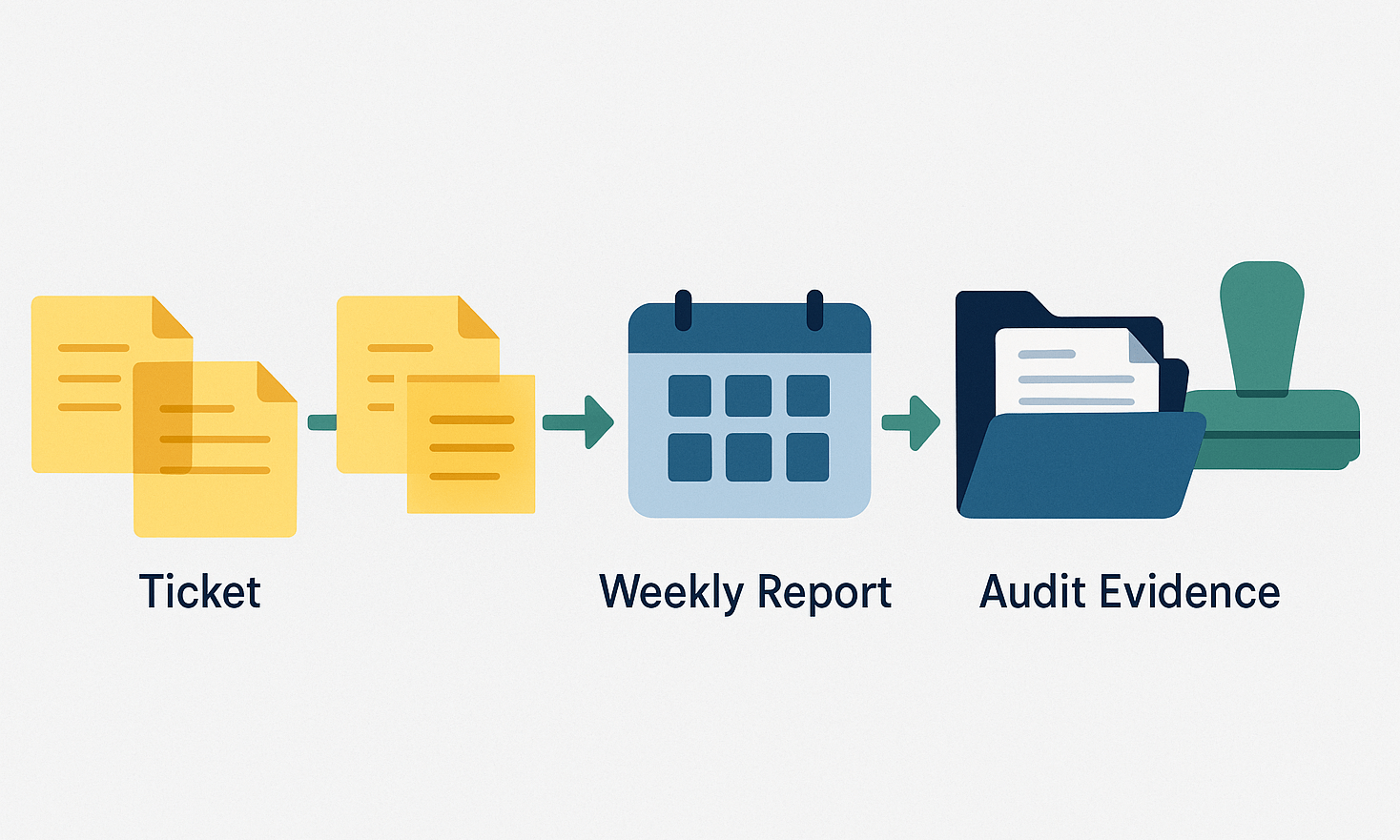
Clear, time-boxed documentation lets auditors verify facts in minutes and helps clients rest easy.
HIPAA’s ongoing-evidence rule (§164.308(b)(1)) makes screenshots and spreadsheets hard to scale. Modern platforms connect to your repositories, cloud accounts, and ticketing queues, then surface gaps in real time.
Independent IDC research shows that trust-management platforms can cut audit-prep time by eighty-two percent and automate up to ninety percent of required evidence collection across frameworks, including HIPAA.
With more than three hundred integrations and one thousand two hundred automated hourly tests, these tools flag drift the moment it appears and hand auditors a ready-made report. For a side-by-side look at two leading trust-management platforms, see this Vanta vs Drata comparison that weighs automation depth, HIPAA framework coverage, and pricing.
Bring the platform online on day one so you start each engagement with a live risk map instead of a blank spreadsheet. Continuous assurance means fewer surprise findings, faster invoices, and a compliance posture clients can watch turn green in real time, safeguard client data, and avoid late-night screenshot sessions.
Trust thrives on proof. HIPAA offers no gold stars, yet §164.308(b)(1) requires continuous evaluation, and buyers expect live evidence. The 2024 Change Healthcare data breach, which had widespread effects throughout the healthcare industry, has highlighted the significant risks associated with third-party vendors.
Broadcast progress in small pulses.
Tiny, regular updates weave compliance into the project story and keep stakeholders calm.
Attach evidence to every control.
Screenshot the SIEM alert, paste the commit hash that enforces TLS 1.3, and link the signed training roster. Clients drop these artifacts straight into their audit folders without a scavenger hunt.
Respond faster than headlines.
Aim to acknowledge incidents within ten minutes and deliver an executive brief within two hours. The average cost for a data breach in the healthcare industry in 2024 was $9.8 million.
Keep this rhythm and you progress from contractor to trusted security ally, the first call when patient data is at stake.
HIPAA is not extra credit; it is the baseline for every healthcare project. When you sign the BAA, you commit to three pillars:
Deliver all three and clients stay focused on patients instead of paperwork, while your work stands out as a competitive edge that keeps both brands off the breach ticker.
Do I need a BAA if I never store PHI, only view it while testing?
Yes. If you create, receive, maintain, or even access PHI on behalf of a covered entity, you’re a business associate and a BAA is required.
What’s the minimum technical baseline clients expect from a HIPAA freelancer?
Full-disk and database encryption, MFA everywhere, least-privilege IAM, TLS 1.2+ (preferably 1.3), centralized audit logs, and a documented backup/DR plan.
How quickly must I report an incident to the client?
Internally: immediately (within hours) per your contract/BAA. Externally: clients have up to 60 days under federal breach-notification rules, so your fast internal reporting enables them to meet that deadline.
Do clients expect cyber insurance from freelancers?
Often, yes. Many require E&O/cyber coverage and proof of controls (e.g., MFA, off-site backups) before engaging, especially if you’ll handle production PHI.

Streamline your Upwork workflow and boost your earnings with our smart job search and filtering tools. Find better clients and land more contracts.